Radiculopathy After Blood Patch
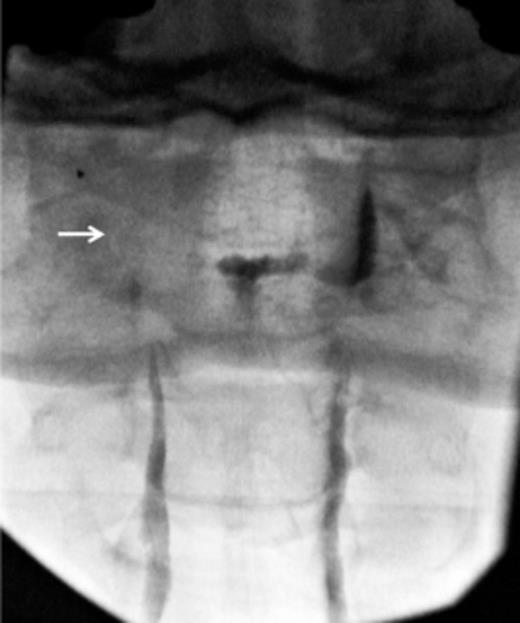
Spinal Headache After Blood Patch
Clinical Features The patient was a 35-yr-old woman without coagulopathy and was initially treated elsewhere for chronic pain by repetitive epidural phenol injections. When the dura was inadvertently punctured during subsequent attempts to inject phenol, immediate epidural blood patch was performed to treat or prevent headache.
The patient developed cauda equina syndrome after six epidural blood patches. The clinical diagnosis was confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging and the intradural haematoma was evacuated surgically. The patient made a complete recovery. Conclusions Epidural blood patch is not without complications. Transient backache and/or radiculopathy may occur in up to one-third of patients receiving a blood patch.
If signs and symptoms continue or worsen, a spinal subarachnoid and/or subdural haematoma should be suspected and neurosurgical opinion sought. The technique used to identify the epidural space is important in preventing subdural injection of blood. The needle should be withdrawn after durai puncture and the epidural space identified at a different level. Blood patches may carry a higher risk of serious complications after multiple epidural phenol injections because of fibrosis and obliteration of the epidural space. Magnetic resonance scans reliably demonstrate the extent of the pathology. If diagnosed and treated before irreversible changes occur, spinal intradural haematoma can result in complete recovery.
Radicular Pain Followed by Epidural Blood Patch Radicular Pain Followed by Epidural Blood Patch Jo, Daehyun; Kim, Eung Don; Oh, Hyun Jin; Oh, Jin Young 2014-09-01 00:00:00 Dear Editor, Postdural puncture headache (PDPH) is a well‐known complication of the epidural block and usually treated by bed rest, intravenous hydration, caffeine and analgesics, and epidural blood patch. The epidural blood patch has been considered as the “gold standard” in the treatment of PDPH and regarded to safe procedure, but various complications, including delayed radicular pain 1 and severe low back pain and lower extremity pain 2 have been reported. We experienced a patient who complained of radiating pain immediately after an epidural blood patch in the lumbar region for PDPH. A 44‐year‐old woman with 2‐year history of chronic low back pain visited our pain clinic due to an exacerbation of low back pain radiating down to the lateral aspect of the right leg from 2 days before. On physical examination, she had a 60‐degree limitation on the straight leg raising test of the right leg because of pain.
There was no other motor or sensory deficit, and deep tendon reflexes were also normal. Under the impression of a herniated lumbar disc at the right L4‐L5 level, we planned to perform a lumbar epidural block with blind technique after getting an informed consent at the L4‐L5 level. Pain Medicine Oxford University Press http://www.deepdyve.com/lp/oxford-university-press/radicular-pain-followed-by-epidural-blood-patch-dBMykYIR9u. Abstract Dear Editor, Postdural puncture headache (PDPH) is a well‐known complication of the epidural block and usually treated by bed rest, intravenous hydration, caffeine and analgesics, and epidural blood patch. The epidural blood patch has been considered as the “gold standard” in the treatment of PDPH and regarded to safe procedure, but various complications, including delayed radicular pain 1 and severe low back pain and lower extremity pain 2 have been reported. We experienced a patient who complained of radiating pain immediately after an epidural blood patch in the lumbar region for PDPH. A 44‐year‐old woman with 2‐year history of chronic low back pain visited our pain clinic due to an exacerbation of low back pain radiating down to the lateral aspect of the right leg from 2 days before.

On physical examination, she had a 60‐degree limitation on the straight leg raising test of the right leg because of pain. There was no other motor or sensory deficit, and deep tendon reflexes were also normal. Under the impression of a herniated lumbar disc at the right L4‐L5 level, we planned to perform a lumbar epidural block with blind technique after getting an informed consent at the L4‐L5 level. Journal Pain Medicine – Oxford University Press Published: Sep 1, 2014. Software update for windows download.